
The heart enables the body to eliminate the unwanted carbon dioxide.

The body’s cells need oxygen to function, and they produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. When blood travels through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, it passes through tiny capillaries that connect on the surface of the lung’s air sacs, called the alveoli. Systolic pressure: This shows how much pressure the blood creates against the artery walls during systole.ĭiastolic pressure: This shows how much pressure is in the arteries during diastole. The high number is the systolic blood pressure, and the lower number is the diastolic blood pressure. When a person takes their blood pressure, the machine will give a high and a low number. Systole: The ventricles contract and pump blood out of the heart as the atria relax, filling with blood again.

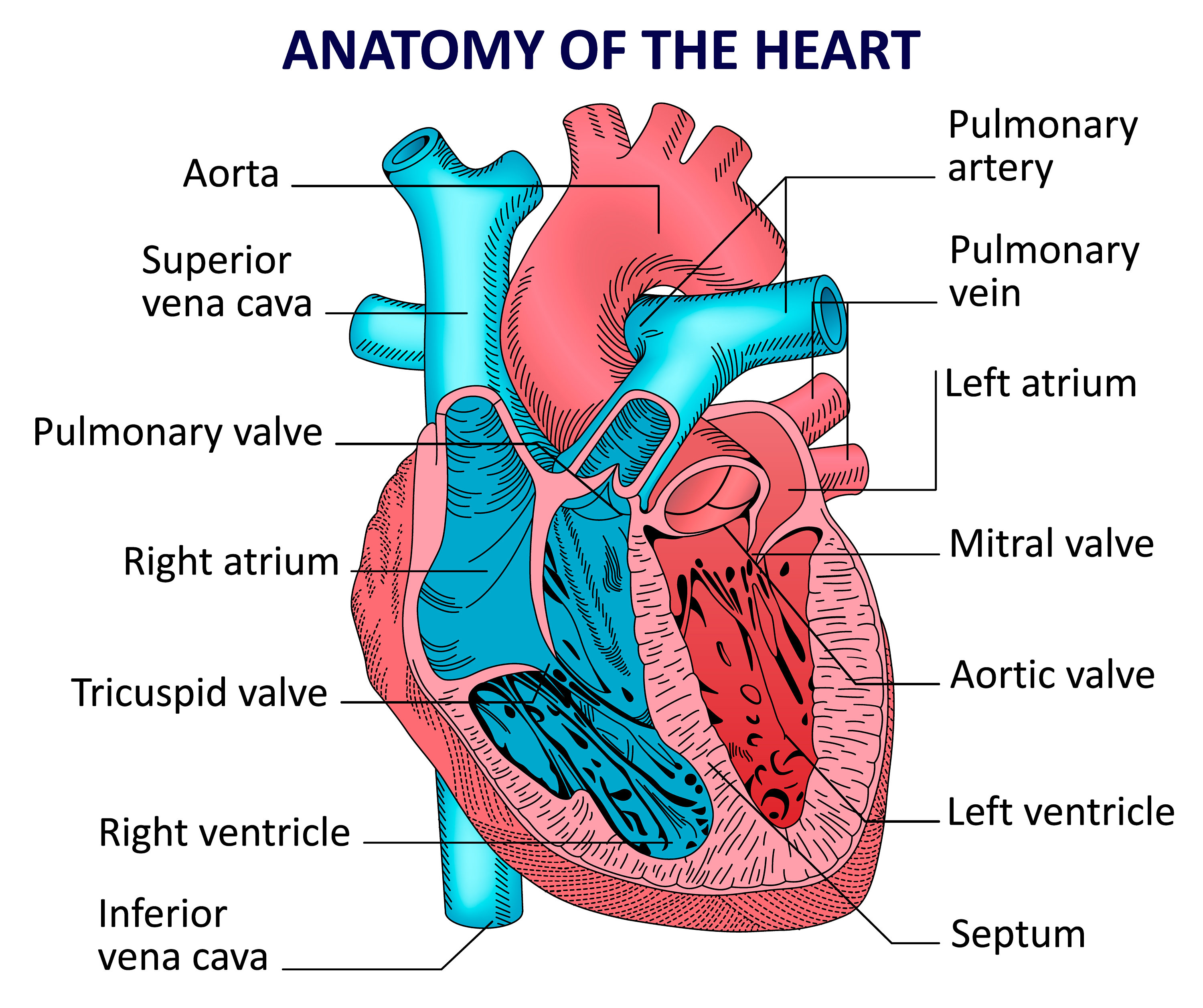
The right atrium contracts, and blood passes to the right ventricle.

The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body through veins called the superior and inferior vena cava.The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood and sends it to the lungs. The atria and ventricles contract and relax in turn, producing a rhythmic heartbeat. The left and right sides of the heart work in unison. Learn more information about a “normal” heart rate here. But this can increase to 100 beats per minute (bpm) or more. The rate at which the heart contracts depends on many factors, such as:Īt rest, the heart might beat around 60 times each minute.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
